Abstract
To cope with the high requirements during the computation of semantic segmentations of earth observation imagery, current state-of-the-art pipelines divide the corresponding data into smaller images. Existing methods and benchmark datasets oftentimes rely on pixel-based tiling schemes or on geo-tiling schemes employed by web mapping applications. The selection of the subimages (comprising size, location and orientation) is crucial since it affects the available context information of each pixel, defines the number of tiles during training, and influences the degree of information degradation while down- and up-sampling the tile contents to the size required by the segmentation model. In this paper we propose a new segmentation pipeline for earth observation imagery relying on a tiling scheme that creates geo-tiles based on the geo-information of the raster data. This approach exhibits several beneficial properties compared to pixel-based or common web mapping approaches. For instance, the proposed tiling scheme shows flexible customization properties regarding tile granularity, tile stride and image boundary alignment, which allows us to perform a tile specific data augmentation during training and a substitution of pixel predictions with limited context information using data of overlapping tiles during inference. Furthermore, the generated tiles show a consistent spatial tile extent w.r.t. heterogeneous sensors, varying recording distances and different latitudes. In our experiments we demonstrate how the proposed tiling system allows to improve the results of current state-of-the-art semantic segmentation models. To foster future research we make the source code publicly available.
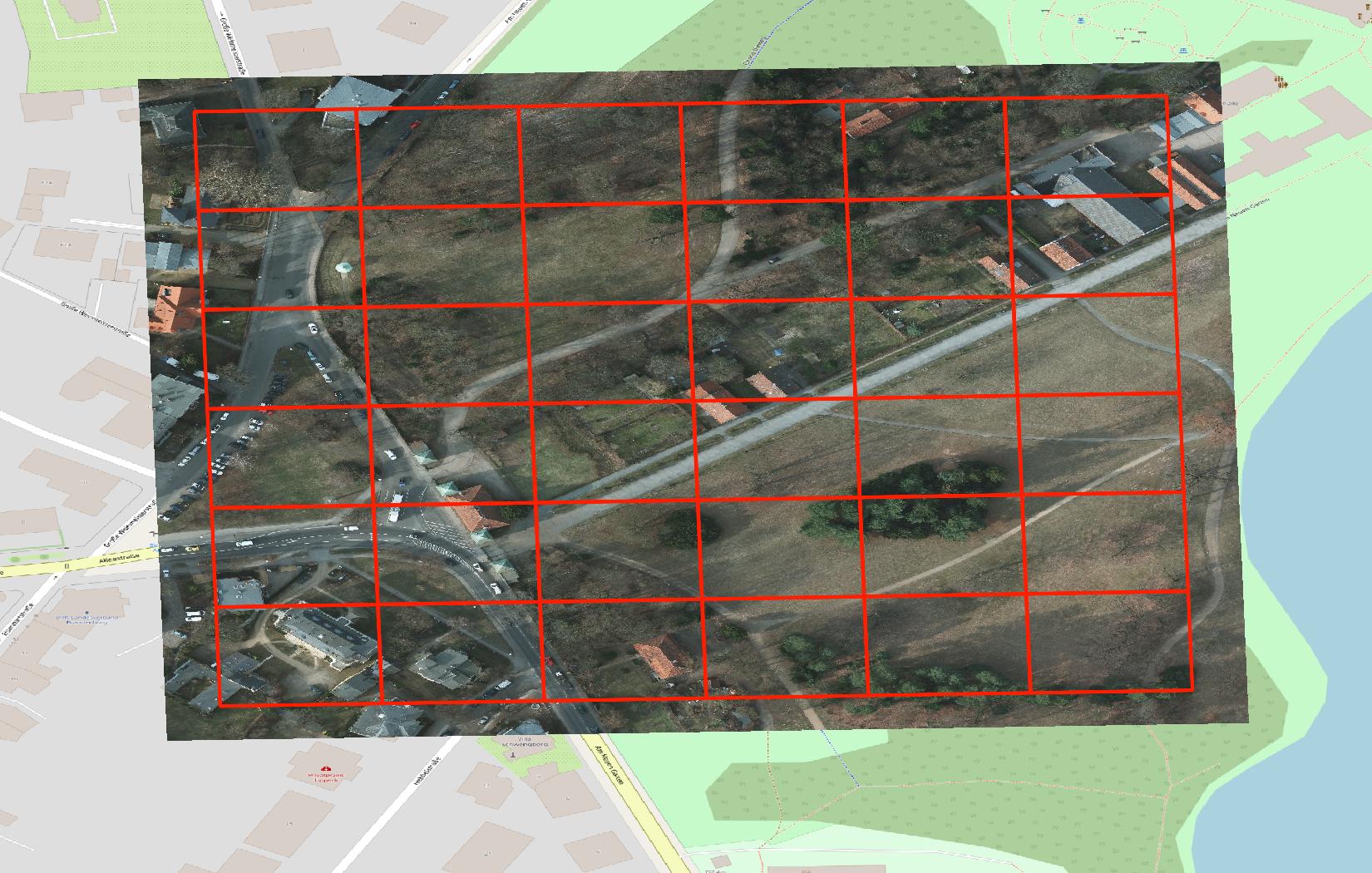
Earth Observation Tiles
Visual comparison of Earth Observation Tiles (left) with a standard web map tiling scheme (right).

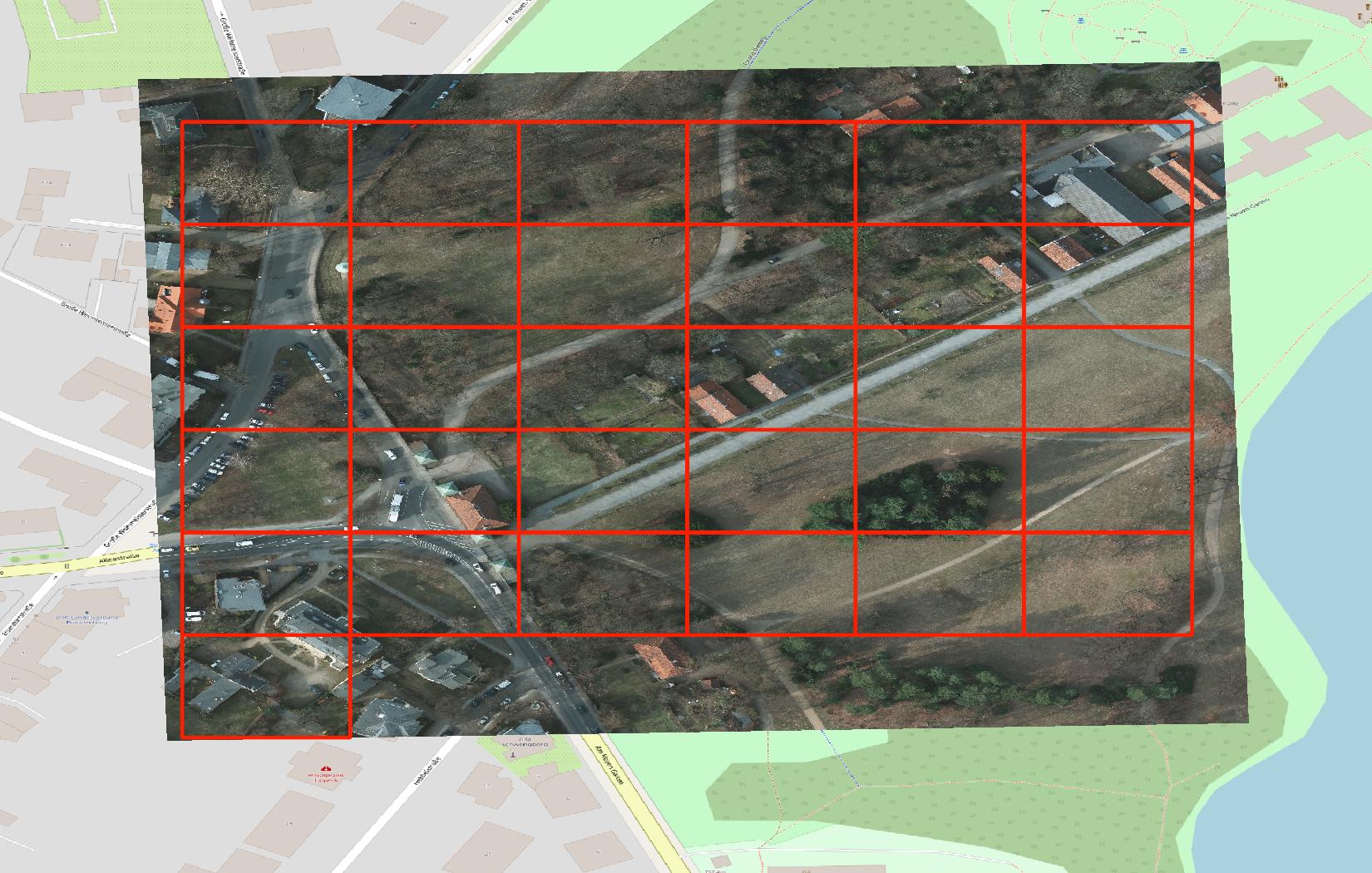
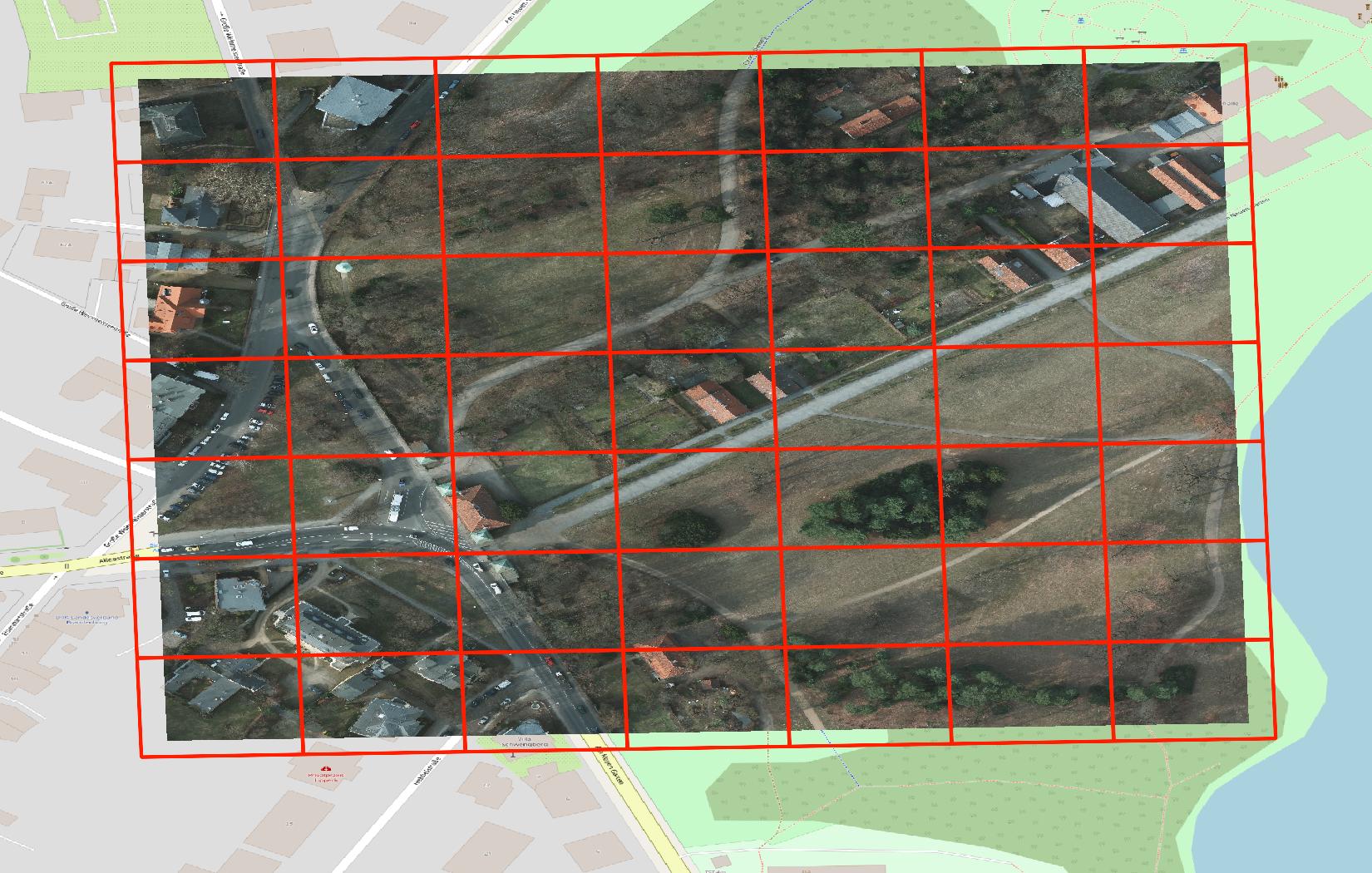
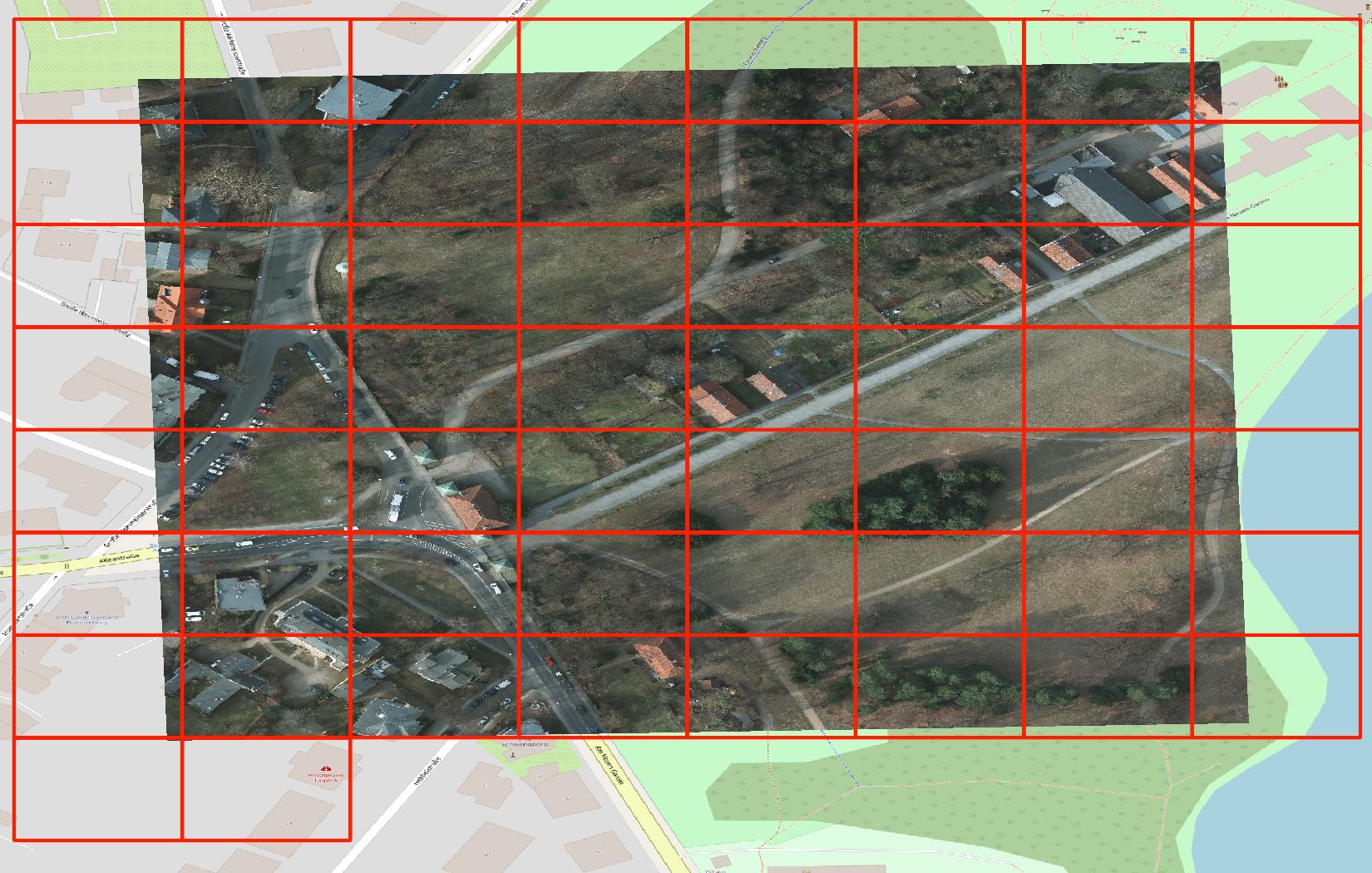
Property comparison of different tiling schemes:
| Tiling Scheme Property | Pixel-based Tiling | Web Map Tiling | Earth Observation Tiling (ours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consistent spatial extent for different sensors | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Consistent spatial extent for different recording distances | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Consistent spatial extent for different latitudes | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Optimal raster image coverage / alignment to raster image | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Customization (e.g. arbitrary granularity or overlap) | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Arbitrary coordinate system support | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Non-normalized raster image support | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
Tile Fusion During Inference Time
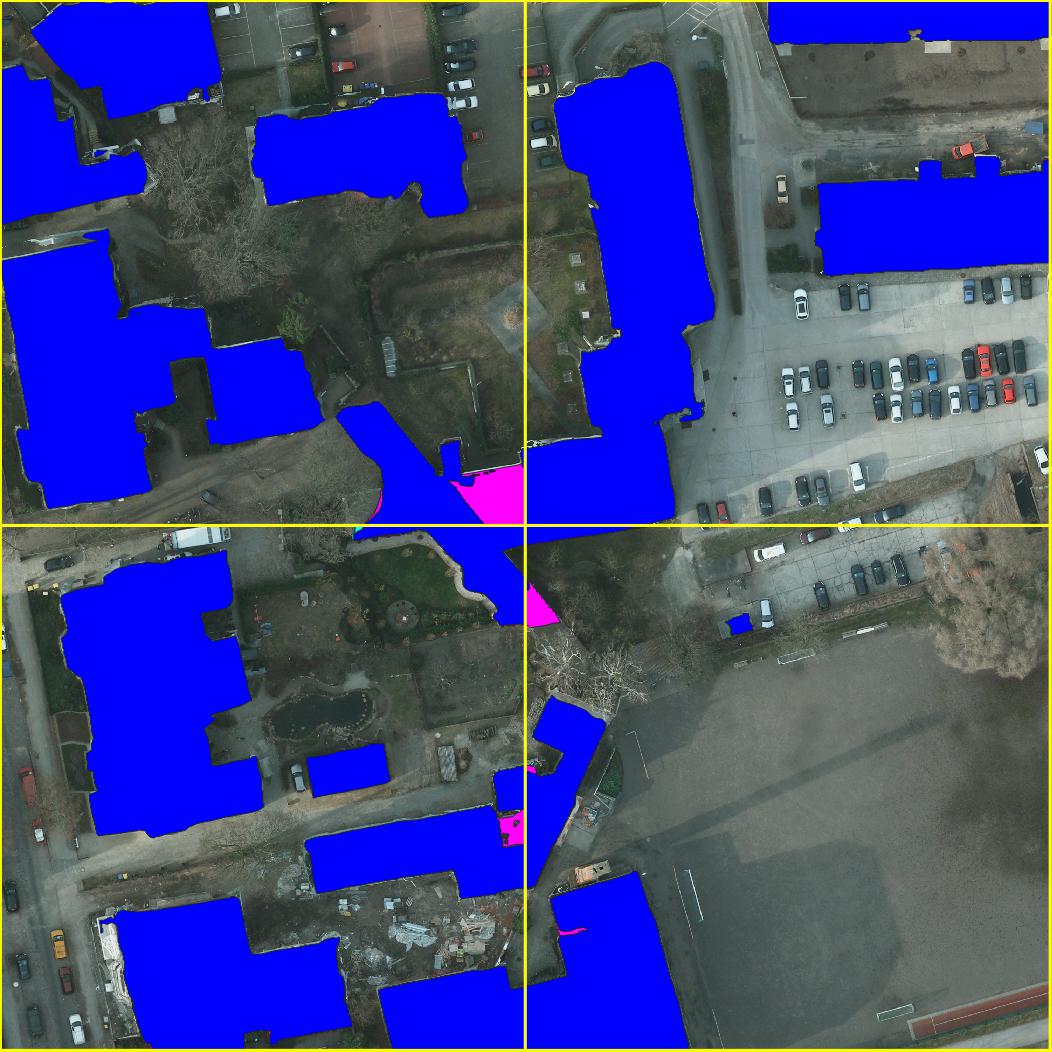

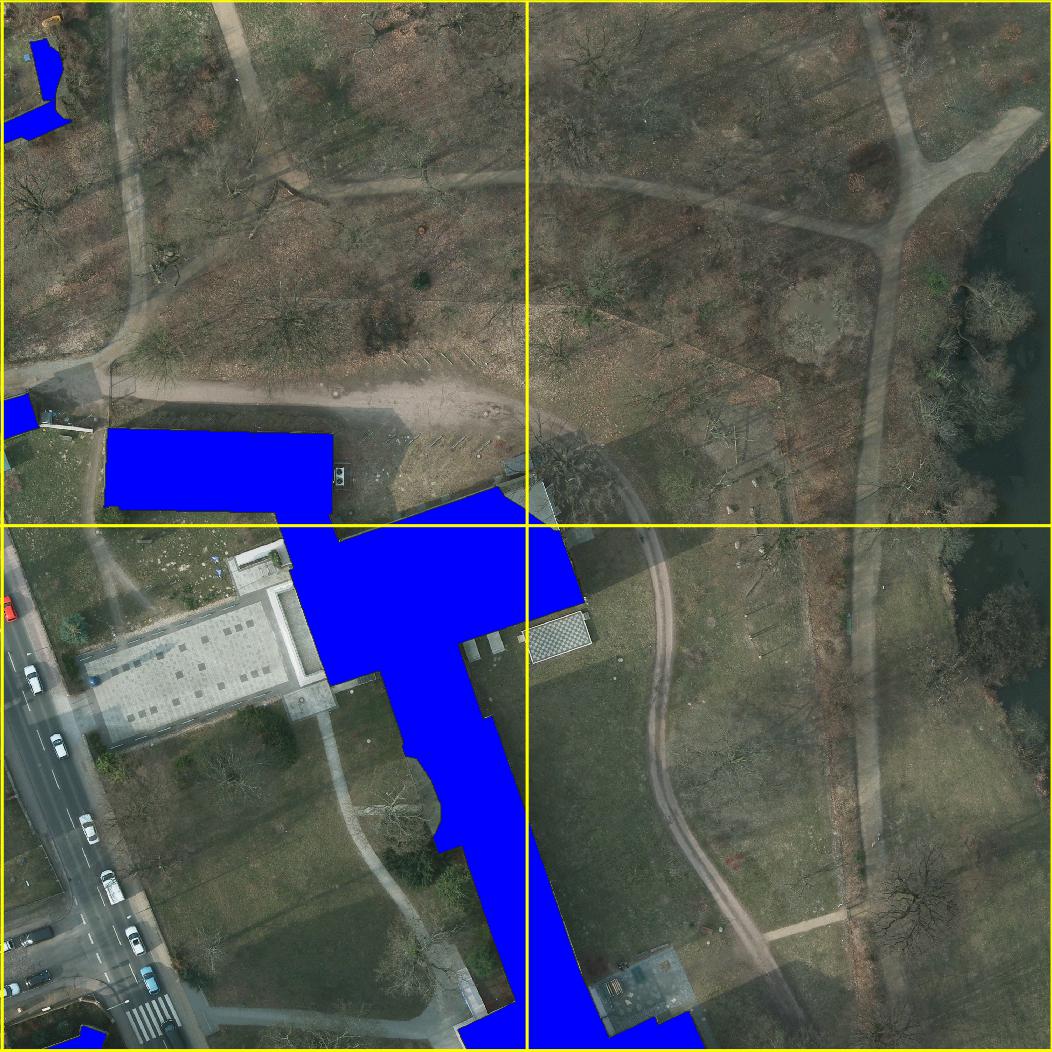
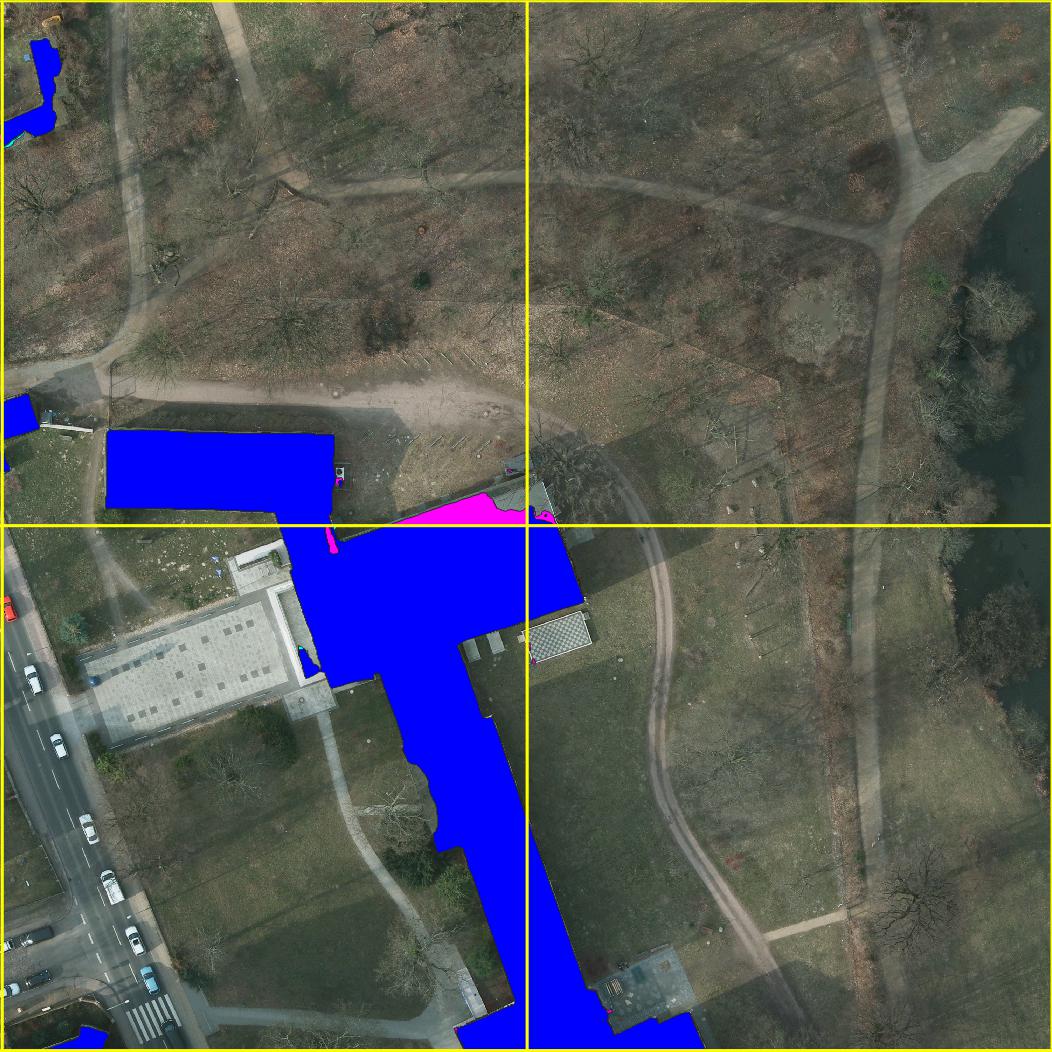

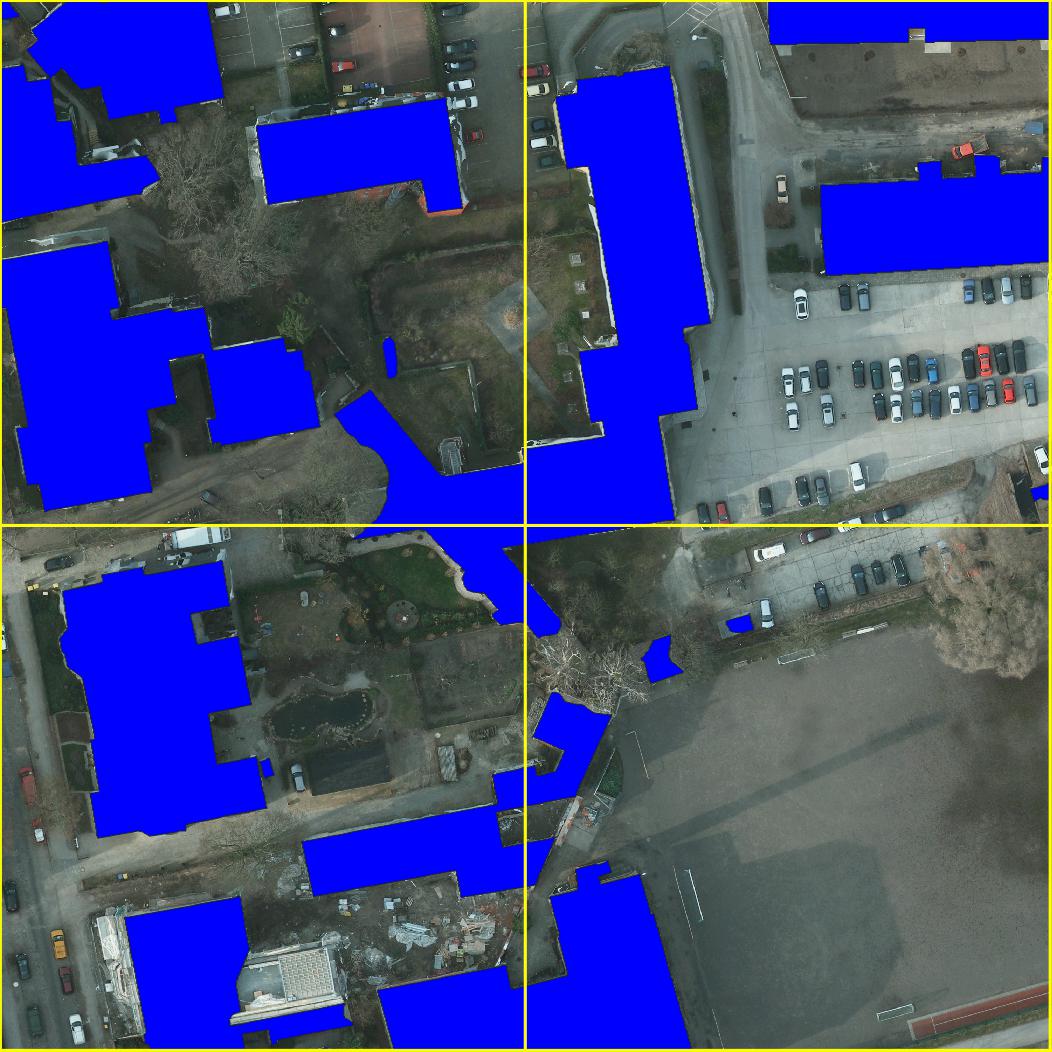


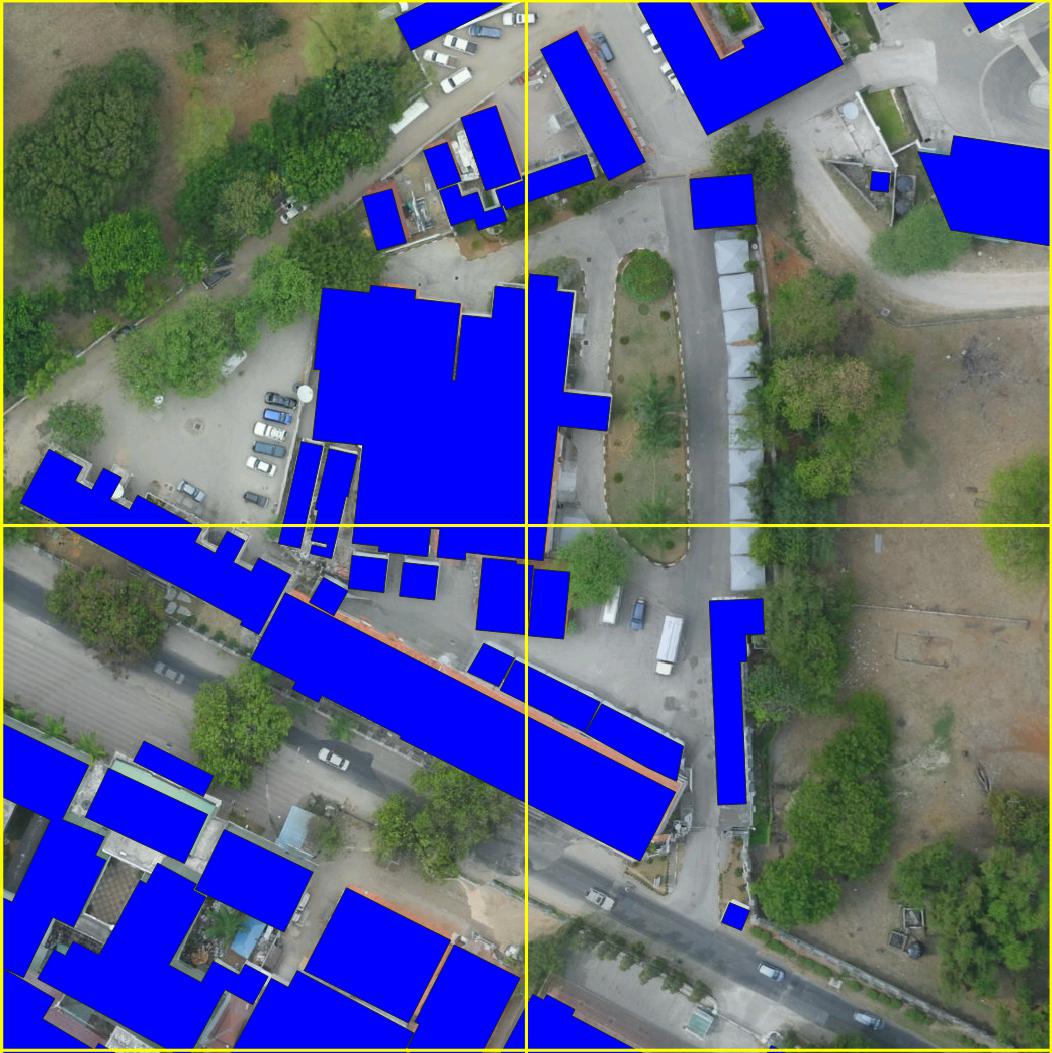
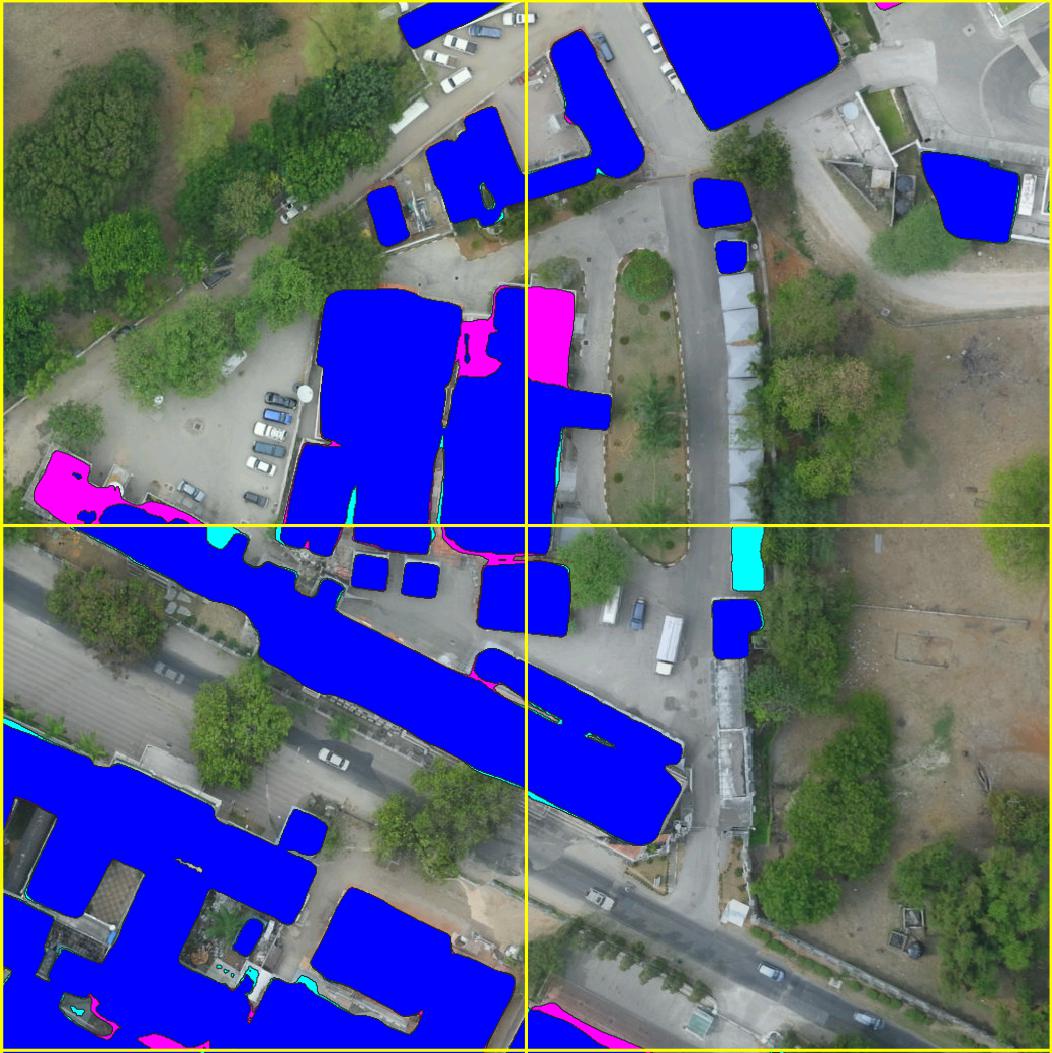



Example Segmentations
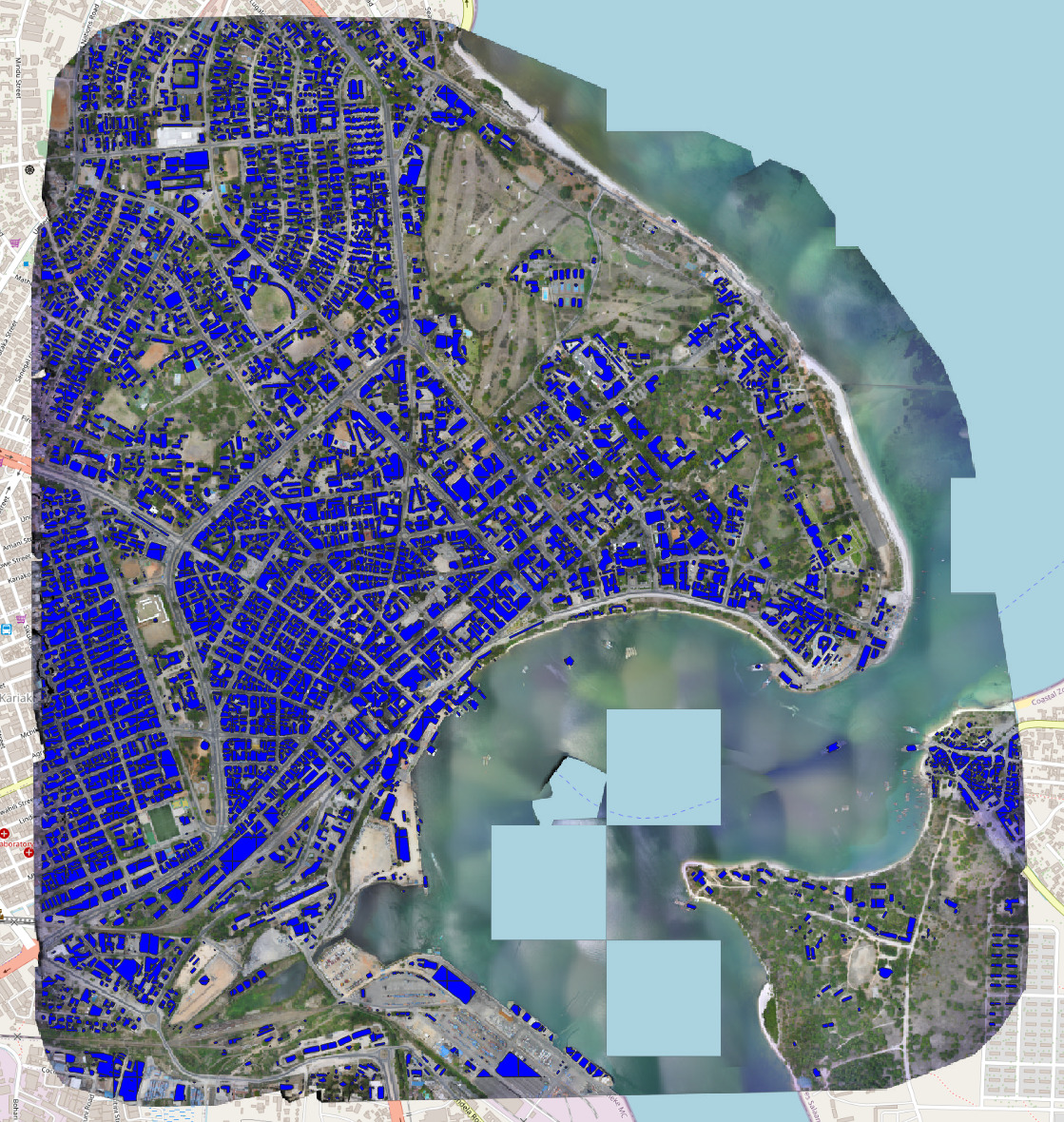
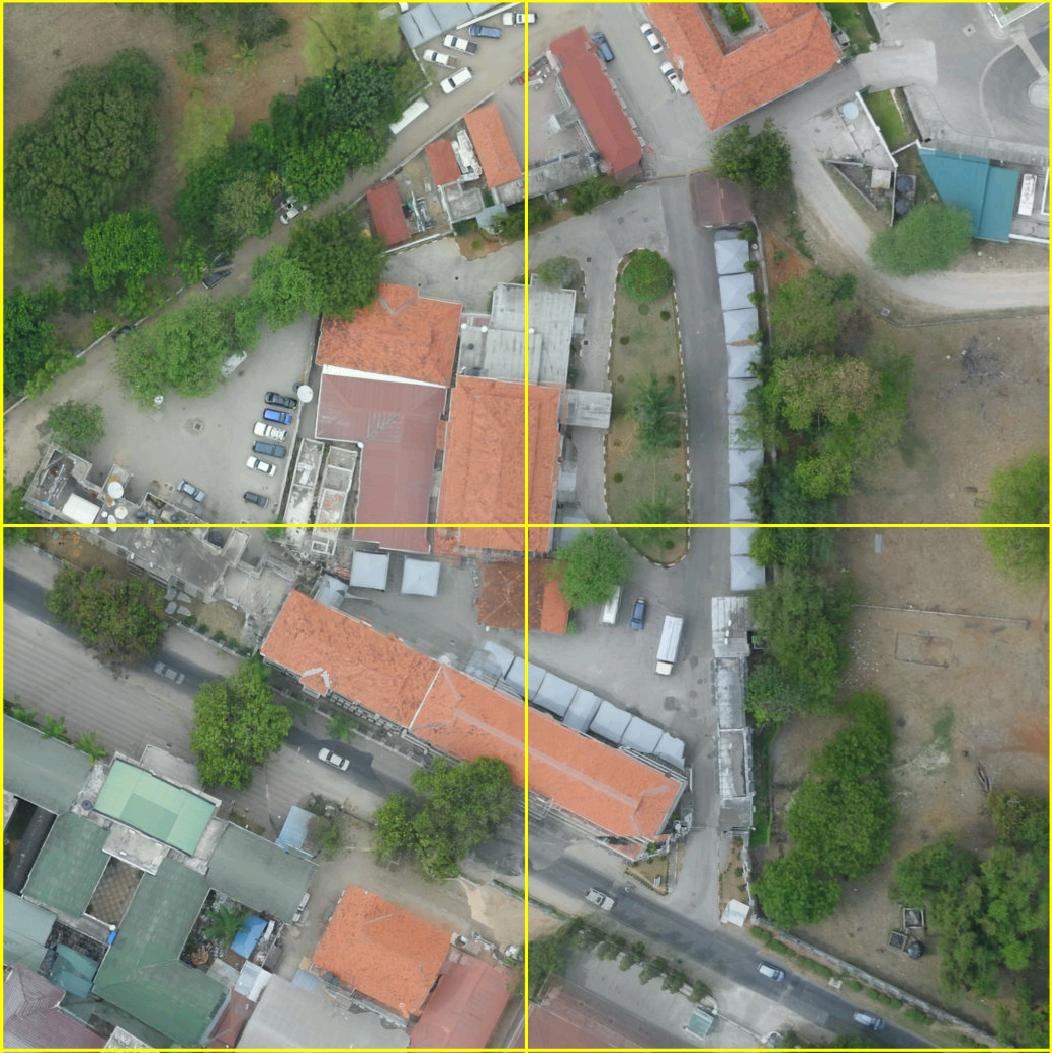
Example semantic segmentation (interactive!) of an area contained in the ISPRS potsdam dataset:
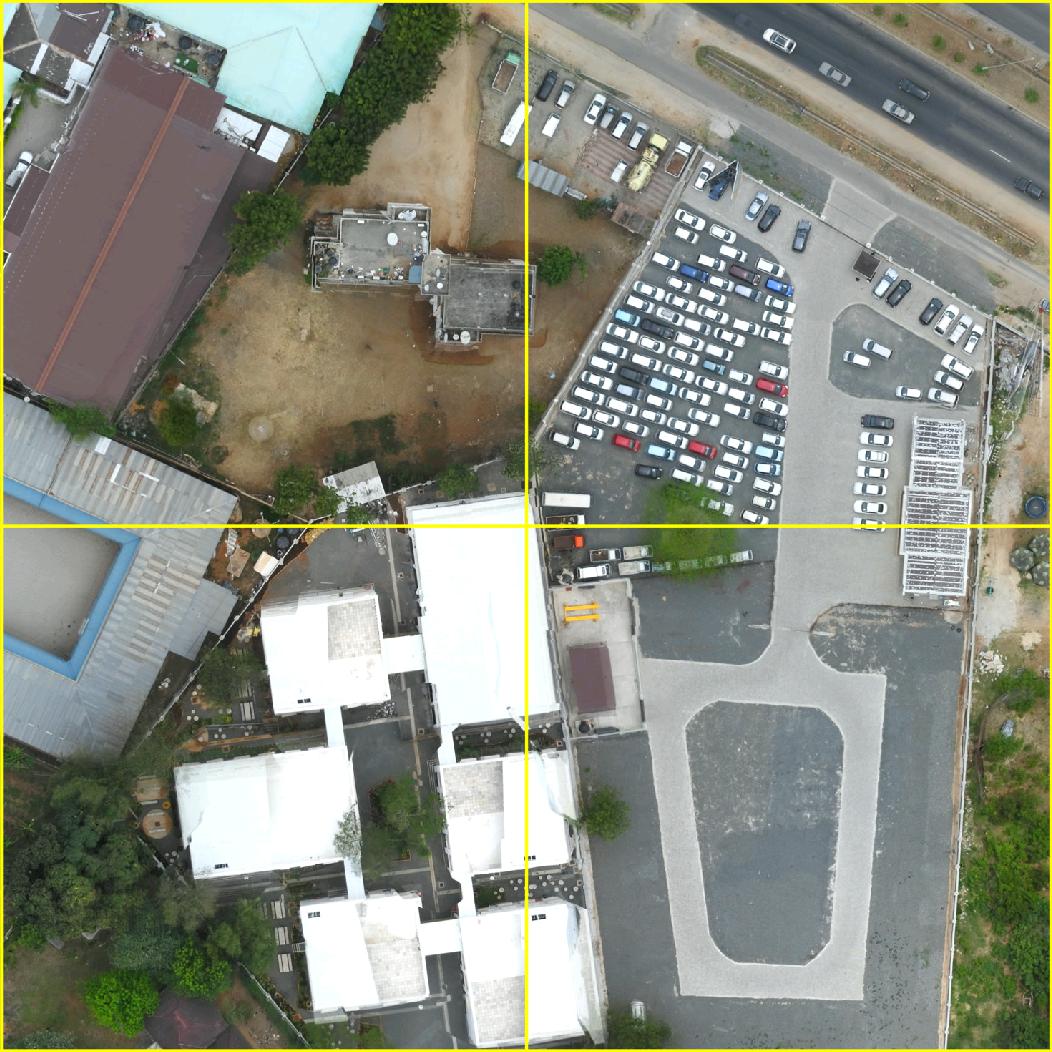
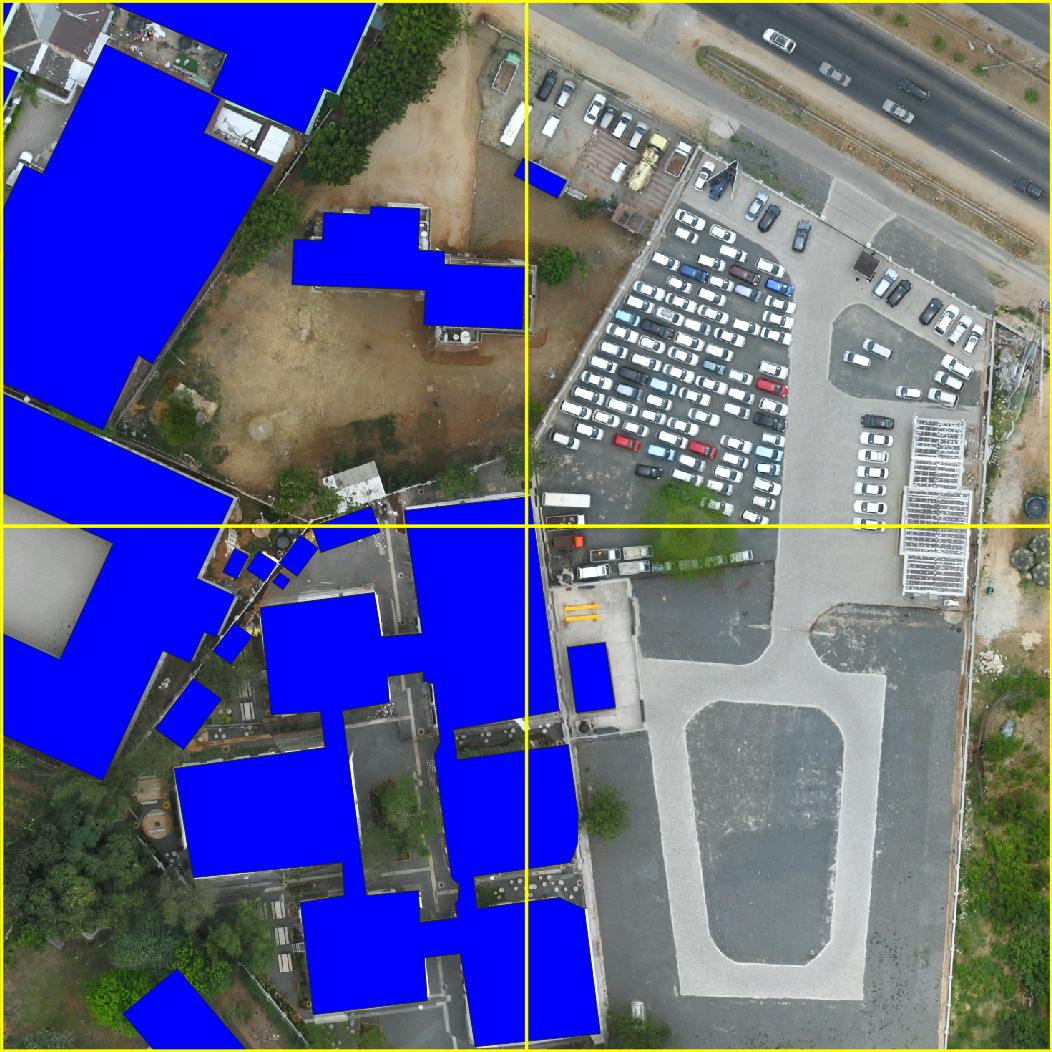
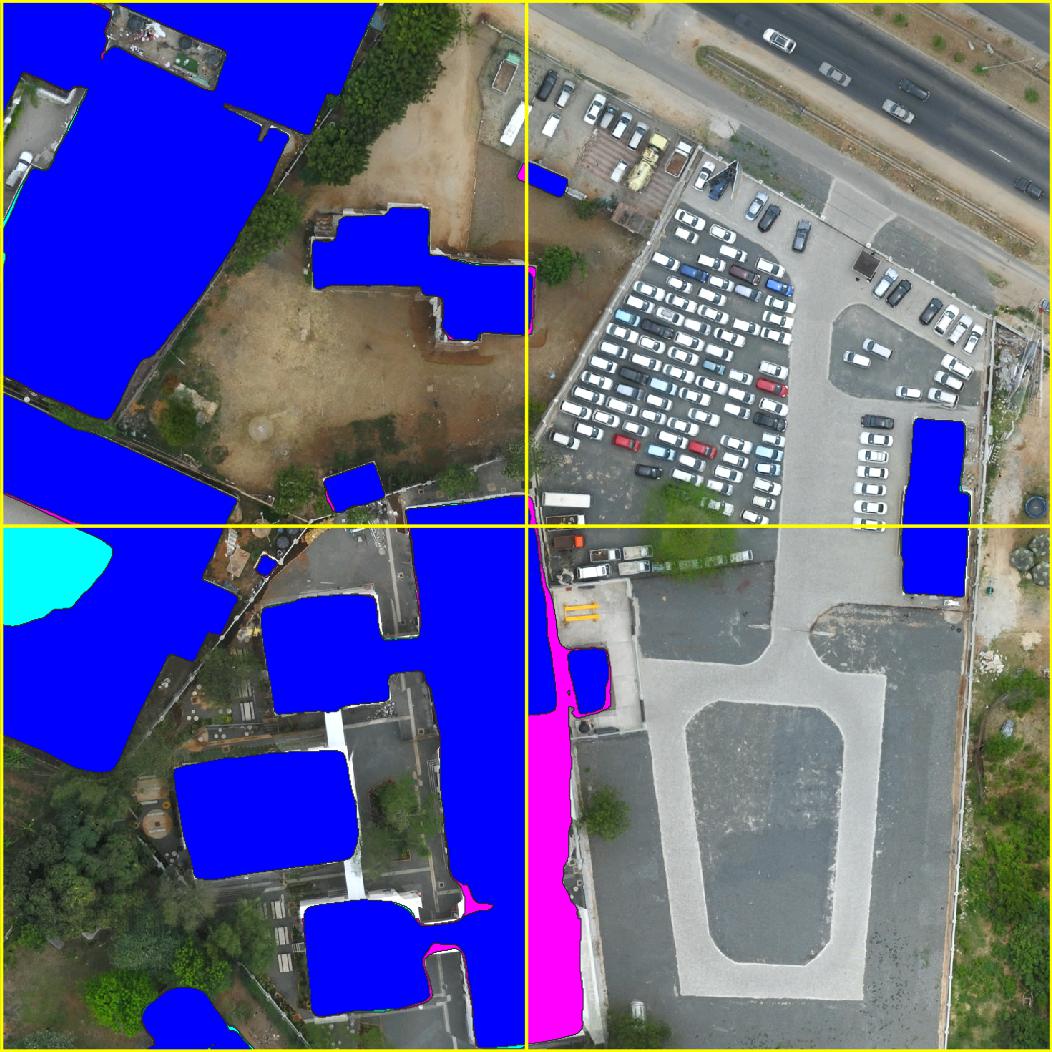
Example semantic segmentation (interactive!) of an area contained in the Open Cities AI dataset: